How to implement RFID technology in your cases
You want to implement an RFID technology into your process or business? Do you know which technology you want to use? There are a few different options that are available. Do you know what they are?
Radio-frequency identification (RFID) uses electromagnetic fields to automatically identify and track tags attached to objects. The tags contain electronically stored information, is a generic term for technologies that use radio waves to automatically identify people or objects.
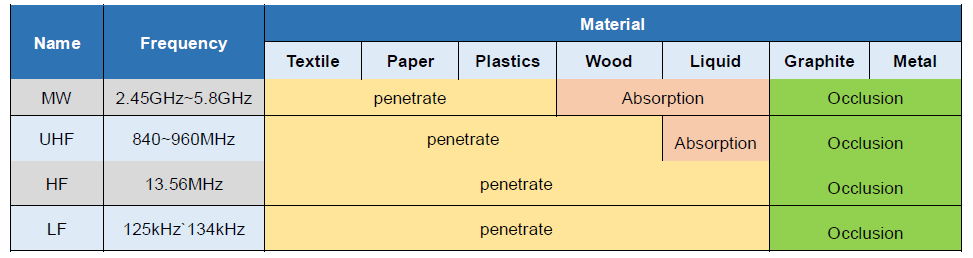
Signaling between the reader and the tag is done in several different incompatible ways, depending on the frequency band used by the tag.
There are two ways to transmit RF signal between the RFID reader and tag, one is inductance coupling, the other is electromagnetic backscattering. Different frequency, the working principle is also different.
RF frequency | Low Frequency(LF) | High Frequency(HF) | Ultra high frequency (UHF) | Microwave |
125kHz – 135kHz | 13.56MHz | 840-960MHz | 2.45GHz | |
Working Principle | inductance coupling | inductance coupling | electromagnetic backscattering | electromagnetic backscattering |
Range | < 60cm | < 1m | 1-10m | 1 ~ 15m |
Characteristics | Without any interference | Short-range read, multi-tag identification | Interference by working environment, Comprehensive performance is the most outstanding | Characteristics similar to UHF, subject to environmental impact |
Tag Type | Passive | Passive | Passive | Active |
Typical Application | Animal Identification factory data collection | Smart cards memory cards microprocessor cards | Access control Retail Transportation and logistics | Freeways toll |
Data Speed | Low speed High speed | |||
Environmental | Dullness Sensitive | |||
Ablility to read near metal | Better Worst | |||
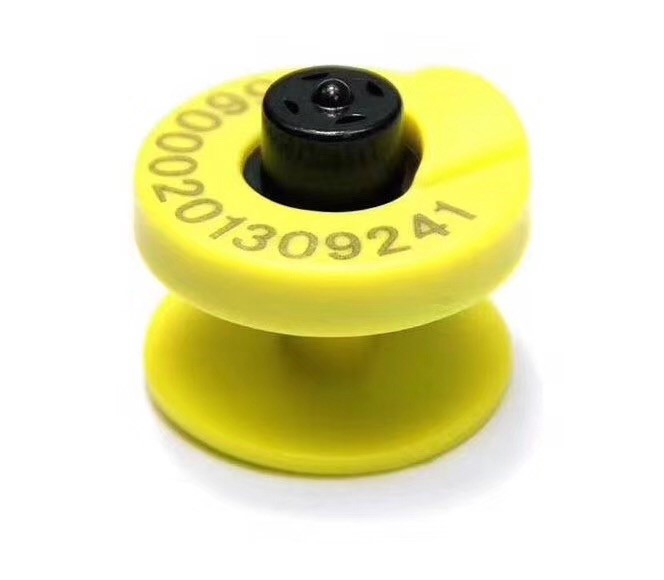
Low Frequency (LF) 125kHz – 135kHz
Generally, the frequency band of low frequency is 10Khz-1MHz, the most commonly used operating frequency is 125kHz and 135kHz. The tags of this frequency band are passive, through the inductive coupling mode for energy supply and data transmission, that is transformer coupling between the coil of reader and the coil of inductor.
Working Features:
- Reading distance < 1m, the storage capacity is 125-512 bits;
- The operating frequency of Ti is 134.2 Khz and the wavelength is about 2500m;
- Data transfer rate is slow;
- Operating frequency not subject to radio frequency control;
- In addition to the impact of metal materials, low-frequency can pass through any object without dropping the reading distance;
ISO/IEC 18000-2, ISO/IEC11784, ISO/IEC11785, DIN 30745
Application
Animal identification, human implantation, tree monitoring, car anti-theft keyless door system, marathon running system, hotel door lock system, access control and safety management system, etc.
Low-frequency systems and read-write devices are more mature, and read-write devices are cheap. However, due to its low resonance rate, the label needs to make a large inductance winding inductance, and often need to package off-chip resonant capacitor, so the cost of its label is higher than other frequency bands.


Hight Frequency (HF)
13.56MHz
The high frequency band is 13.56 Mhz, with a wavelength of approximately 22 M. Although the magnetic field region of the frequency drops rapidly, it is able to produce a relatively uniform read-write region. High Frequency label products are the most extensive, with higher transmission speed and distance, but the cost is also more expensive than low frequency label.
These HF tags typically have a good amount of memory and come in all sorts of different sizes and shapes. These tags are good for applications where read distances are close, a maximum of ~1.5 meters. The other positive factor for this is the frequency range and technology are recognized globally.
Working Features:
- Data transmission is fast, the typical value is 106Kbit / s;
- Storage Capacity: 128 bits -8K;
- Support password security or microprocessor;
It is most used in RFID application;
In addition to the impact of metal materials, can pass through any object, but the reading distance drops.
ISO/IEC 15693, ISO/IEC 14443 A, ISO/IEC 14443 B
Application
Passport, E-visa, ID card, driver’s license, bus card and other identification applications, high-frequency applications mainly for library management, gas cylinder management, clothing production line and logistics system management, hotel lock management, conference staff access system, medical logistics system, intelligent shelf management.
NFC
Near Field Communication typically uses a smartphone or tablet that has NFC capabilities. Read ranges are typically ~1.6 inches or closer. NFC devices are used in contactless payment systems, similar to those used in credit cards and electronic ticket smartcards and allow mobile payment to replace/supplement these systems. This is sometimes referred to as NFC/CTLS (Contactless) or CTLS NFC. NFC is used for social networking, for sharing contacts, photos, videos or files. NFC-enabled devices can act as electronic identity documents and keycards. NFC offers a low-speed connection with simple setup that can be used to bootstrap more capable wireless connections

3 Ultra high frequency (UHF)
840 ~ 960MHz
The common operating frequency of UHF is 860-928MHz, but the global standard varies. UHF systems transmit energy through an electric field. The energy of the electric field does not drop very quickly, but the area being read is not well defined. The reading distance of this band is quite far, range up to about 10m. At the same time, the Inlay is relatively inexpensive because it be made in etching or printing.
The application system of liquid goods in UHF still not mature, disturbed by the human body, and the price of reading and writing equipment are more expensive, also a high cost for the application maintenance cost, but it is widely used.
Working Features:
- Long reading range, fast transmit speed;
- Multi-tag identification;
- Mainly suitable for 3-10m of application accasions;
- The primary frequency band for Internet of things;
- The radio waves can not transmit through matter such as water, dust, fog, etc;
ISO/IEC 18000-6C, ISO/IEC 18000-6B
Application
Retail, Government, Entertainment & hospitality, Manufacturing, Transportation, Healthcare, Commericial services, access control, sports, waste management, etc.

Working Environment Effects: air humidity, air particles, wall blocking, metal
Goods impact: moisture content, goods placement
Microwave (MW)
433MHz 2.45GHz, 5.8GHz
Microwaves are used in frequency bands above 1Ghz, with common operating frequencies of 2.45Ghz and 5.8Ghz. Microwave band is similar in characteristics to applications and ultra-high bands, with long read distances, but more sensitive to the environment.
Working Features:
- Active tag;
- Can be used in complex environments such as tunnels and mountains;
- Label stabness and fireability
- Long transfer distance, up to 100 meters
- With battery, high cost
Application
Applications such as high-speed non-parking charge (ETC), motor vehicle remote control locking system (RKE), real-time positioning system (RTL) and personnel management.







