
Mastering Automated Transportation with AGV and RFID
RFID, as a type of automatic identification technology, has very obvious advantages in its application on AGV carts. First, RFID has a strong resistance to other environmental factors, such as oil pollution, water, dust, and electromagnetic interference, so it is very suitable for the working environment of the production workshop. Secondly, RFID technology is quite mature, with low maintenance costs and simple technical construction, making it more advantageous in actual operation. For these reasons, the application of RFID site recognition on AGV carts is becoming more and more widespread. In addition, RFID can improve the work efficiency of AGV carts, making their role in the production process more important, thereby creating greater value for enterprises.
What is AGV technology?
AGV is an abbreviation for Automated Guided Vehicle, meaning “automatically guided transport vehicle.” This is a wheeled mobile robot that can run along wires, marking blocks, or magnetic strips on the ground, or through visual or laser navigation. It is mainly used for the transportation of materials and goods in workshops and warehouses in industrial production. With the arrival of Industry 4.0, more and more enterprises are beginning to pay attention to and widely apply AGV. Currently, AGV is used in production lines, warehouse storage, inbound, line-side, storage, picking, packaging, sorting, outbound, loading and other scenarios.
AGV can automatically charge, has a high degree of automation, convenient operation, small footprint, and can freely travel within the production workshop, has great flexibility, and has been widely used in e-commerce, express delivery, warehousing and sorting, automobiles, tobacco, medicine, 3C, clothing and other types of enterprises and manufacturing industries.
AGV is characterized by wheeled movement, compared to walking, crawling, or other non-wheeled mobile robots, it has the advantages of speed, high efficiency, simple structure, easy control, and safety. Compared with other equipment commonly used in material transportation, AGV does not require fixed tracks or brackets, and is not restricted by sites, roads, and space. Therefore, in the automated logistics system, AGV can maximize its automaticity and flexibility, achieve efficient, economical, and flexible unmanned production.
Why is RFID technology used on AGV carts?
The main reason for using RFID on AGV carts is to achieve more accurate goods recognition and path navigation. The RFID reader can read the position information in the RFID landmark and drive the AGV cart along the set route through the PLC controller.
Traditionally, Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) mainly rely on fixed magnetic tape for navigation when handling materials. However, this method is less flexible, easily disturbed by surrounding metal materials, and difficult to meet the needs of complex routes. In this context, the emergence of Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) technology provides new possibilities for the navigation and handling work of AGV carts.
RFID technology is a non-contact smart recognition technology, which has the characteristics of fast read-write speed and short read-write time, and can read and write moving objects. Therefore, using RFID tags as marking stations on magnetic navigation routes can conveniently plan the route of AGV carts, achieve the optimal route, and thus significantly improve the performance of AGV carts.
In addition, the application of RFID technology in AGV automated transport has good environmental adaptability. It can accurately identify RFID tags through site positioning, thereby achieving navigation control of AGVs. By embedding RFID tags in the navigation magnetic strip, AGV carts can read station tags, determine their location based on the current tag, read tag information, choose the correct path, or search for the optimal path according to the algorithm, to save the time required for transportation.
It is worth mentioning that the positioning advantage of AGVs using RFID is very obvious. First, RFID is less disturbed by other environments, such as oil pollution, water, dust, and electromagnetic, so it is more suitable for the working environment of the production workshop. Second, RFID technology is very mature, with low maintenance cost and simple technical construction, so the application of RFID site recognition and positioning in AGV carts is also widespread. It can be predicted that with the continuous development and progress of technology, RFID will play an increasingly important role in the application of AGV carts
RFID technology has the following significant advantages in automated guided vehicle (AGV) site identification:
1.Real-time monitoring and recording of work information: One major advantage of RFID technology is its ability to monitor the working state of AGV vehicles in real time and record their work information in detail. This detailed monitoring and recording ability is crucial for understanding transport routes, avoiding possible delays or errors, and ensuring the smoothness and efficiency of the transport process.
2.Quick and accurate identification of location information: RFID technology can quickly and accurately identify the location information of AGV vehicles, which is crucial for ensuring the accuracy and efficiency of the transport process. Especially in the event of a malfunction, RFID technology can quickly check and locate the fault to facilitate timely repairs, reduce losses in the transport process, and ensure the smooth operation of the production line.
3.Intelligent management: Another major advantage of RFID technology is its ability to intelligently manage AGV vehicles. With RFID technology, we can automatically obtain data and flexibly control the activities of vehicles, thereby improving work efficiency, reducing manual intervention, and enhancing the efficiency and accuracy of the transport process.
4.24-hour uninterrupted work: RFID technology enables AGV vehicles to work 24 hours without interruption, significantly enhancing the level of automation in production and transport. By reducing labor costs and improving work efficiency, RFID technology helps to enhance a company’s transport capacity and competitiveness.
How exactly does an AGV trolley implement intelligent RFID positioning and navigation?
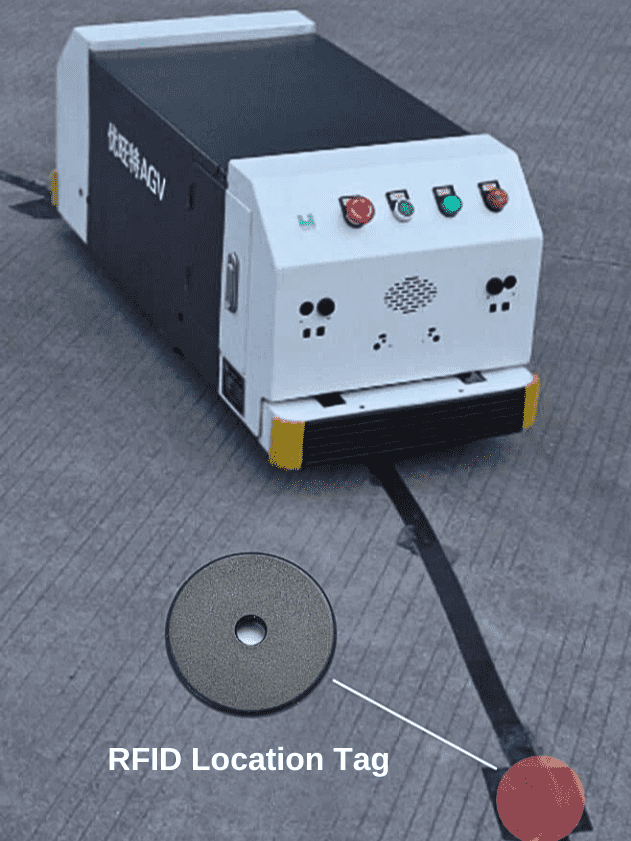
An RFID reader/writer is installed on the AGV trolley, and AGV landmarks (RFID electronic tags) are installed at each node of the driving track. When the AGV car passes through a node during work, the RFID will automatically obtain the material/product information pre-entered on the AGV landmark (RFID electronic tag), guiding the AGV to make corresponding actions and timely deal with related issues. When the AGV transports goods within the factory and passes through various nodes, the RFID reader/writer will automatically collect RFID landmark information and transmit it to the backend management system in real time. The backend management system will obtain the node position information associated with the identified RFID landmark ID and display it in the software system.
- Install an RFID reader under the front of the AGV feeder car. Place goods such as pallets, racks, and bins on the feeder car for transportation. The RFID reader will identify the RFID landmarks on the track nodes, thereby selecting stations for feeding and implementing the AGV dispatching system function and station positioning function.
- AGV transportation mainly uses pallets as carriers. The use of RFID technology in AGV goods transportation mainly involves installing a reader/writer and antenna on the AGV landmark card reader, and installing RFID tags on the pallet or goods. The pallet and goods record the information of the managed items.
- RFID landmarks with station codes are installed at the track nodes on the material transportation route. After placing the materials on the AGV feeder car, the control center will issue instructions (transportation routes) to the PLC controller. After receiving the instructions, the PLC controls the feeder car to start and begin transporting materials according to the instructions.
- After the RFID reader recognizes the location information stored in the RFID landmark, it will feedback to the PLC controller (control system module). After receiving and processing the encoded data, the PLC will control the AGV feeder car to select a station to park according to the feeding route. The AGV makes corresponding actions (changing speed, turning, positioning, and parking, etc.) by reading the ground mark with RFID.
- After the materials reach the station, the AGV feeder car can transport materials to the next station according to the instructions. Therefore, after the feeding command is completed, the feeder car will return to the starting point along the set route.
RFID in AGV Automated Transportation Collection Application
In the process of industrial production, especially in production line management and pharmaceutical sorting line management, RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) technology plays an extremely important role. First, we install RFID readers at the corresponding industrial nodes. On the product pallet or the product itself, we have RFID tags that have entered product information. During the production process, when the product with the RFID tag passes through the industrial node, the industrial RFID reader will read the product information and then upload this information to the computer (information system management) for management and analysis.
The transportation installation method of the AGV (Automated Guided Vehicle) cart is different from the production line management method. We install the RFID reader on the AGV cart, and the RFID tags are installed on the track nodes where the AGV travels. When the AGV cart travels to the label, the industrial reader can read the label information, and then judge the next step and the direction of the AGV cart based on the obtained label information, such as whether to go straight or turn.
Finally, intelligent warehouse management also uses RFID technology. We bind RFID tags to the materials in the warehouse, and the industrial RFID readers are installed on the transportation equipment. When the transportation equipment travels to the warehouse materials, the industrial reader will read the label information on the materials, and after confirming that the information is correct, the transportation equipment will move the materials to a new location for storage. In this way, we can achieve precise management of warehouse materials and greatly improve logistics efficiency.
What are the applications of RFID and AGV in the industrial field?
- Raw Material Transportation and Handling
Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) play a pivotal role in industries such as paper making, textiles, steel, rubber, and plastics. These vehicles automatically transport raw materials from the warehouse to the production line, making the production process more efficient and orderly.
- Mobile Assembly Applications
In mobile assembly applications, AGV vehicles replace traditional production lines. They carry core production components, completing all the processes from movement to installation, until the product assembly is complete and put into storage. The application of this technology greatly enhances production efficiency.
- Pallet or Shelf Transportation
In manufacturing or distribution centers, AGV vehicles transport shelves or pallets filled with parts, and automatically move them to the designated destination. These intelligent vehicles can automatically lift (or pull) pallets, and automatically put them down when they reach the designated place. This mode of transportation is widely used in manufacturing and warehouse logistics systems. To achieve these operations, AGVs need to be equipped with lifting devices.
- Finished Product Automatic Transportation
For the automatic transportation of finished products, the requirements for AGV vehicles are more stringent. For example, acceleration and deceleration during transportation must be smooth, and the loading and unloading of goods need to be more precise to prevent the goods from being damaged during transportation. Usually, this type of transportation uses towing, drum, or forklift AGVs.
- Automatic Docking Applications of Production Lines
AGV vehicles also play an important role in the automatic docking applications of production lines. They automatically unload semi-finished or finished products from the production line and transport them to the designated destination. For example, they can automatically transfer semi-finished products between production lines, or automatically store finished products. To complete these tasks, AGV vehicles usually install drum devices.




AGV selection RFID tags can be divided into low frequency (LF), high frequency (HF), ultra-high frequency (UHF), What RFID sensor is used for AGV?
The working frequency of RFID tags has a direct impact on the working principle of the RFID identification system. This includes whether to adopt inductive coupling or electromagnetic coupling principles. At the same time, the working frequency also determines the recognition distance of the equipment. In addition, the difficulty of implementation and the cost of RFID tags and readers are closely related to the working frequency. The frequency division of RFID applications is usually located in the internationally universal ISM radio frequency band. Within this range, there are multiple working frequencies, including 125kHz, 134kHz, 13.56MHz, 860-960MHz, etc.
According to different working frequencies, RFID tags can be subdivided into three categories: low frequency (LF), high frequency (HF), and ultra high frequency (UHF). The working principles of RFID in different frequency bands are different. For example, RFID electronic tags in the LF and HF bands generally use the principle of electromagnetic coupling. For UHF RFID, it generally uses the principle of electromagnetic transmission. In practical applications, the widely used frequencies are distributed in 3 bands, which are low frequency 125kHz~134kHz, high frequency 13.56MHz, and ultra-high frequency 860-960MHz. Each frequency has its own characteristics, so it is used in various different fields. In order to use RFID technology correctly, it is necessary to choose the appropriate frequency according to the specific scene.
- 125KHz~134.2KHz low-frequency RFID landmark tags are an important application. It is mainly used for site identification of AGV (Automated Guided Vehicle) automatic feeding vehicles and meal delivery robots. This tag is small in shape, similar to a coin, and has good durability. Its shell is encapsulated with ABS material, suitable for various outdoor environments, and can be installed by burying, which is very convenient.
- 13.56MHz high-frequency RFID landmark tag is another common application. This tag is made of PPS material, its shape is also similar to a coin, and it has anti-metal properties. It has the advantages of high temperature resistance and corrosion resistance, and can be used in scenarios such as fixture tray tracking, asset control, and AGV site landmark identification. The main use is as an AGV station positioning tool based on RFID navigation. The AGV car recognizes the landmark card information through the landmark sensor to recognize the station or path to complete automatic driving. This tag is specially used for AGV unmanned handling station identification and patrol robot path recognition system applications.
- 860-960MHz ultra-high frequency RFID landmark tags are used for site identification of AGV automatic feeding vehicles and AGV meal delivery robots. The reading distance can reach 2.5m, it supports multiple tags to be recognized at the same time, and data encryption and permanent locking can also be performed, providing high security. Also, this tag uses 3M adhesive, making the installation process very simple and convenient.
