Active RFID vs. Passive RFID: What’s the Difference?
RFID electronic tag is the common name of radio frequency identification (RFID), which consists of a tag, an interpreter and a data transmission and processing system.
Generally divided into active RFID and passive RFID, memory with antenna chips, the chip stores information that can identify the target.
The most mature application of RFID technology lies in the management of warehouses, logistics and supply chains to identify the advantages of long distance, fast, not easy to damage, large capacity and other bar codes, which can simplify the complicated process of traditional logistics and transportation, and improve the efficiency and transparency of cargo circulation.

Application of RFID Tag.
Whether it is active RFID or passive RFID, its role is to identify goods, but their application scenarios are not the same, in the traditional logistics system, active RFID because of the strong signal, the coverage is relatively wide, generally used in warehousing. Passive RFID is often used in transportation, strictly controlling shipments and security.
Passive RFID application scenario Passive RFID technology warehousing is mainly used to track or monitor the shipment of pallets, packaging boxes and goods entering and leaving the warehouse. When warehousing, the goods may already have RFID tags, or they may need to initialize the tags, enter the cargo information, and then paste it on the goods.
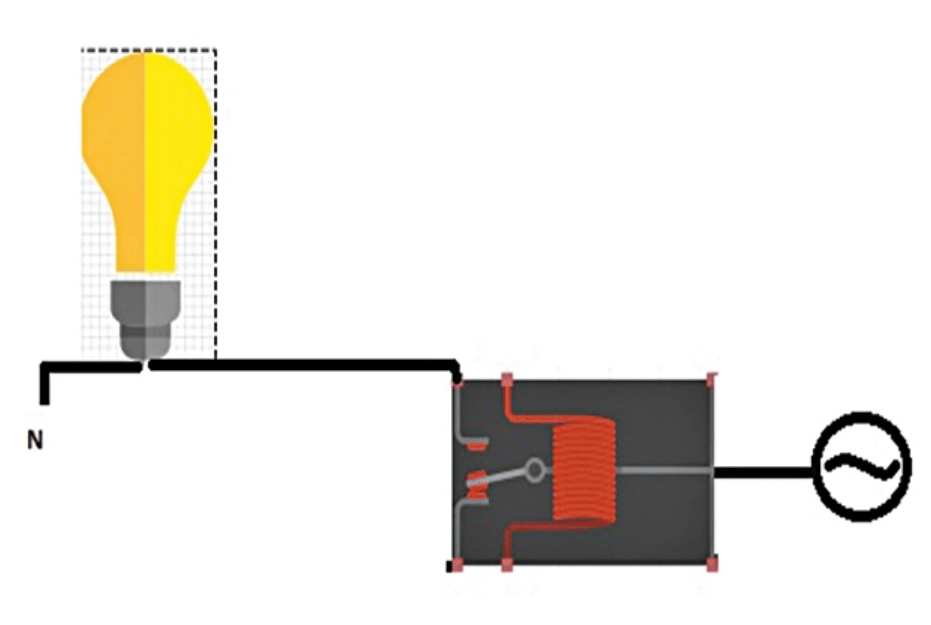
In the traditional logistics and transportation mode, every time the goods arrive at a transit station, they need to scan the terminal code to confirm that the goods have accurately arrived at the operation center.
If there are different goods on the same car, most of them will use passive RFID tags, because the sensing range of passive tags is relatively small, within 60cm, by scanning one by one, there will be no scanning induction errors.
Specific cases can refer to e-commerce logistics, each piece of goods to the operation center, there will be a special person to scan and identify one by one. The advantage of this method is that the data is accurate and the error is small, and the disadvantage is that if the goods are scattered, the time and cost of scanning one by one are high, and it is easy to damage and lose the goods.
Active RFID application scenarios Active RFID is placed in the warehouse need to monitor and track the goods in the area, according to the site environment in accordance with the radio frequency planning, the deployment of active readers, to ensure the coverage of the range and signal strength, and wireless LAN wireless access point planning is the same reason.
Active RFID sensing range can be as high as 30 meters, since this high-frequency output sensing is so strong, why can not be used for in-transit transportation? The reason is that the current pallet electronic tags are only used for induction identification, and can not analyze and manage the information of the goods, using active RFID sensing, the terminal can not read what the goods on the car are, and it is also very prone to induction errors.
Therefore, in the traditional logistics system, active applications are used in warehousing, and passive applications are used in transportation.
Active RFID and passive RFID have their own advantages and disadvantages, can only be used in specific scenarios, the role is greatly limited. Under the concept of plate transportation, procurement, manufacturing, warehousing, distribution, pallets will follow the flow of goods. If the label on the pallet can be compatible with both active RFID and passive RFID, it can bring great convenience to transportation and warehousing.
What Is An Active RFID Tag?
Active electronic tag refers to the energy of the tag work provided by the battery, the battery, memory and antenna together constitute an active electronic tag, different from the passive radio frequency activation method, before the battery replacement has been through the set frequency band external information.

What Is A Passive RFID Tag?
The performance of passive RFID tags is greatly affected by tag size, modulation form, circuit Q value, device power consumption, and modulation depth. Passive RF tag 1024bits memory capacity, ultra-wide working frequency band, not only in line with relevant industry regulations, but also for flexible development and application, can read and write multiple tags at the same time. Passive RF tag design, no battery required, memory can be repeatedly erased more than 100,000 times.

So, What’s The Difference Between Passive And Active RFID Tags?
ACTIVE RFID
|
| PASSIVE RFID
|
433MHz and 2.45GHz | FREQUENCY | 860-960MHz |
Up to 150 meters | READ RANGE | Up to 15 meters |
Typically $15 to $ 40 | COST | Less than $1 per tag |
Smaller than business card | TAG SIZE | Mini size 5*5mm |
Medium to very large | ASSET SIZE | Very small to very large |
Oil, Gas, Construction, Mining | INDUSTRY | Healthcare, Manufacturing, retail |
Screws, rivets, zip ties, welding | ATTACHMENT METHOD | Adhesives, epoxy, zip tie, welding, hanging |
Internal Battery | POWER | Powered by RF waves |
Batteries last 3-5 years and typically can’t be changed | PAIN POINT | Less effective around water and metal |
SUMMARY
Active RFID system
- Extremes long read range
- Increase tag abilities with partner technologies (gps, sensor, etc)
- active RFID tag come with battery (3-5years batter life)
- some active tag may have a sensor too, (track environments, track moisture leves temperature, climate, heart beat, etc)
Passive RFID tag
- smallest tag
- much cheaper
- Thinner/Flexible
- High at just able range
- tag come with long lifetime
The Classification Details of Passive RFID Tag
High Temperature – Certain industries, like healthcare, track the number of cycles that instruments undergo in punishing autoclaves. Specific passive RFID tags are designed to withstand extreme temperatures and accommodate for those types of applications, among others.
Rugged – Applications in outdoor environments or tough warehouses need a tag that can withstand snow and ice, dust and debris, or even the crushing forces felt under a tractor wheel. For these applications, a highly rugged passive tag is needed to make the application successful.
Size – Some applications have specific size constraints when tracking small or large items. Size is one of the more important questions to answer when choosing an RFID tag because there are many different sizes available.
Materials – If an application requires tracking metal assets, UHF metal-mount tags may be the only option. These tags are specifically designed to mitigate the problems UHF RFID faces around metal.
Embeddable – If tagging an item becomes a problem for specific applications due to significant wear and tear, embeddable tags can fit in small crevices and be covered in epoxy so the RFID tag is out of harm’s way.
A roll of Passive RFID inlays
Inlays are usually the cheapest RFID tags costing as low as $0.12 per tag in high volumes, but the price does not affect the performance. These inlays are grouped into three main types:
Dry Inlays – An RFID microchip (IC) and antenna attached to a material or substrate called a web. These inlays look like they have been laminated and come standard with no adhesive.
Wet Inlays – An RFID microchip (IC) and antenna attached to a material, usually PET or PVT, with an adhesive backing. Most of the time these inlays are clear and can be peeled off their roll and immediately stuck on an item.
Paper Face Tags – These are essentially wet inlays with a white paper or poly face. These are ideal for applications that need printed numbers or logos on the front for identification.




